| Glossary of Home Construction Terms |
|
|
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z
- Abstract of title
- A summary of the history of the title to a particular piece of property. Should contain a summary of the original grant and all subsequent conveyances and encumbrances affecting the property. The professional doing the abstraction will certify that the history is complete and validated.
- Acre
- Land equal to 43,560 square feet, 4,840 square yards, 4,047 square meters, 160 square rods or 0.4047 hectares.
- Acceleration Clause
- A statement in some mortgage deed that allows the lender to make the entire debt due immediately if the borrower defaults on a payment or other condition of the loan. Be sure to check your mortgage loan for this clause.
- Adjustable Rate Mortgage (ARM)
- This mortgage has an interest rate that changes with movements in the index. ARMs are also referred to as AMLs (adjustable mortgage loans) or VRMs (variable rate mortgages). Also see CAP
- Aerobic Biological Oxidation
- Reducing the pollution or oxygen demand of organic substances in water via a waste treatment process utilizing organisms in the presence of air or oxygen.
- Aerobic Organism
- Any organism that requires oxygen.
- Aerobic Treatment
- Aerobic processes include rotating biological contactors, extended aeration and trickling filtration. They are processes in which microbes decompose complex organic compounds using the liberated energy of in the presence of oxygen for reproduction and growth.
- A-frame design
- Style that features a steeply peaked roofline and a ceiling that is open to the top rafters.
- Agent
- Substance, force, radiation, organism, or influence that affects the body whether the effects are beneficial or injurious.
- Agricultural Pollution
- Substances and wastes, both liquid and solid, that leach or runoff farms. Includes animal manure and carcasses, crop residues, fertilizers, feed and erosion and dust from plowing, pesticides.
-

- Airborne Particulates
- Suspended particulate matter found in the atmosphere as solid particles or as liquid droplets, i. e., windblown dust, emissions from industrial processes, smoke from the burning of wood and coal, and the exhaust of motor vehicles.
- Alarm Systems
- Warning devices, installed or free-standing, including but not limited to: carbon monoxide detectors, flue gas and other spillage detectors, security equipment, ejector pumps and smoke alarms.
- Allergens
- Allergens are substances that cause allergic reactions. They include pollens, dust particles, mold spores, food, latex rubber, insects, insect feces, animals or medicines.
- Allergy
- A specific reaction of the immune system to a seemingly harmless substance that does not bother most people. People who have allergies often are sensitive to more than one substance. Many people are allergies that are undetected due to the mildness of their symptoms or lack of or lack of sophication of testing.
- Aluminum Wire
- Conductors made of aluminum for carrying electricity. Because of to its lower conductivity and fragility, aluminum wire is generally limited to the larger Wire sizes. Aluminum wire is lighter and less expensive than copper but is not as good a conductor.
- American Foursquare
- American Foursquare (1900-1925) style is features a simple box shape, two-and-a-half stories, a four-room floor plan, low-hipped roof and a deep overhang, a large central dormer, full-width porch and wide stairs with brick, stone or wood siding. (also Prairie Box & Bungalow)
- Amortization
- Scheduling payments of a loan in equal installments that consist of changing ratio of principal and interest.
- Aquifer
- Wells are considered aquifers - they are porous geological structures below the surface carrying or holding water.

|
|
|
|
- Architectural Services
- Any practice involving the art and science of building design for construction of any structure or grouping of structures and the use of space within and surrounding the structures or the design for construction, including but not specifically limited to, schematic design, design development, preparation of construction contract documents, and administration of the construction contract.
-

- Art Deco
- Art Deco was the first widely popular style in the United States to break with the revivalist tradition (See Gothic Revival or Greek Revival or Italianate). Art Deco characteristics include vertical emphasis, steel frames, flat roofs, setbacks (step-like recessions in a wall) emphasizing the geometric form, string courses, geometric ornamentation such as, parallel straight lines, zigzags, chevrons, lozenges (diamond-like shape, but not a square), abstracted floral motifs, stylized figure sculpture, octagonal lamps, clocks, sunrise and floral patterns in ornamentation, intense colors in terra cotta, glass, colored glazed bricks, mosaic tiles, and colored mirrors, stepped frontispiece and stepped window head, volutes in door surrounds, strips of windows with decorated iron grille work in surrounds to add vertical feeling, metal windows, sashes, and casements.
- Argon Gas windows
- See Low-E Windows
- Asbestos
- Mineral fiber that when inhaled can cause cancer or asbestosis. Banned or severely restricted its use in manufacturing and construction by the EPA. Cleanup of asbestos require safety gear and professinal training to assure that cleanup and disposal standards are met.
- Asbestosis
- Disease, associated with chronic exposure to and inhalation of asbestos fibers, caused by that causes breathing to become progressively more difficult and can lead to death.
 |
ASHI |
- ASTM
- American Society for Testing and Materials International is one of the largest voluntary standards development organizations in the world-a trusted source for technical standards for materials, products, systems, and services. Known for their high technical quality and market relevancy, ASTM International standards have an important role in the information infrastructure that guides design, manufacturing and trade in the global economy. cite: astm.org
- Automatic Safety Controls
- Devices designed and installed to protect systems and components from unsafe conditions.
- Backfill
- Material used to refill an excavation, or the process of doing so.
-
Backwashing

- Reversing the flow of water in order to clear or clean a filter
- Baffle
- Deflect substances - changing the flow of air, water or other matter. Baffles are used to deaden sound.
- Balusters
- Balusters are small posts that support the upper rail of the balustrade.
- Balustrade
- The entire railing system including a top rail and, if present, the bottom rail is called the balustrade.
- Balloon Framing
- Balloon framing is most usually seen in older homes. The wall studs start at the base of the building and are continuous to the attic. Horizontal bracing members are nailed to the studs.
- Bargeboards
- Also called gable rafters, bargeboards are more elaborately carved and ornamented.
|
|
|
- Belfry
- A room at or near the top of a tower which contains bells and their supporting timbers.
- Bell Bottom Pier
- A Bell Bottom pier is a vertical structural support built to support concrete slab foundations and is built of concrete and steel rebar. Its name is derived from the bottom of the pier, which resembles a bell and provides a greater area of support for the pier and the concrete slab above it.
- Beneficiary
- (1) The person for whom a trust operates or in whose behalf the income from a trust estate is drawn. (2) The lender in a deed of trust and security of note transaction.
- Biodegradable
- Sustance or material that will degrade easily.
- Biodegradability
- The rate at which a substance or material can be broken down by bacteria or other environmental factors.
-

- Biotecture
- The art of combining architecture and biology with the goal of liveable sustainability in the design and structure of buildings and environments.
- Blackwater
- Wastewater from toilets, latrines, privies, water containing feces or body fluids and water from sinks used for food preparation or disposal of chemical or biological ingredients. See greywater.
- Bloom
- (1)Plants: first appearance of budding. (2) Algae: a mass of algae in a body of water often indicating presenceof pollutants
- Board and Batten Siding
- Siding composed of wooden boards applied vertically, creating a barn-like exterior. Batten slats cover the wall joints in the siding. Boards are usually 8 to 12 inches wide.
- Board Foot
- A cubic measurement of lumber. One board foot = 144 cubic inches. (1 foot long X 1 foot wide X 1 inch thick) To calculate board feet, the thickness in inches is multiplied by the width in inches, dividing the total by 12 and then multiplying that by the length of the board in feet. (For example, if your board measured 24 inches wide by 2 inches thick by 13 foot long, you would multiply 24 X 2 = 48. Divide 48 by 12 = 4. Multiply 4 by 13 = your board would equal 52 board feet.)
- Board Insulation
- Insulation in various rigid forms, such as: Polystyrene, rigid fiberglass, polyurethane, or isocyanurate.
- Bog
- Generally poorly draining land that appears wet and spongy, highly acid and rich in plant residue. The result is lake eutrophication (nutrient pollution).
- Borescope
- Ideal for critical inspection of typically inaccessible areas. Consists of a rigid tube with an eyepiece on one end, an objective lens on the other linked together by a relay optical system in between. Borescopes may be fitted with a magnifying device and a way to illuminate the work being inspected.
- Boxed Eaves
- Boxed eaves are a simple cornice treatment where the eaves of a pitched roof are boxed in with wood and have few other details.
-
BTU

- British Thermal Unit: A measurement of heat. The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 pound of water from 63° F to 64 F.
- Building-Related-Illness
- Term used to describe more precisely what is popularly known as "sick building syndrome" or the indoor transmission of infectious agents. Use as a more accurate term suggests that buildings cannot truly be described as being "healthy" or "sick", that buildings do not transmit sickness.
- Bungalow
- Bungalow-style homes with their open floor plans, built-ins and fireplaces were low, functional, spreading house. (See American Foursquare)
- Buttress
- Buttresses, generally made of brick or stone are built against a wall to support or reinforce it. Flying buttresses are free-standing, but attached to the main structure by an arch or a half-arch.
- Buy-down
- A creative method for helping new or first-time home buyers afford a home purchase. Monthly payments are set at a reduced rate for the first few years of the mortgage loan. Be sure to fully understand the terms of any buydown you are considering. Although family incomes generally rise over time, it's important to know your family's future earning power - and to anticipate the higher loan payments in future budgeting. Remember to plan for changes in family income that may result from one of the earners attending school, or becoming unavailable for employment due to child care or elder care needs.
- BX Cable
- Armored cable is insulated conductors inside a flexible metallic covering. BX should not be used where it may be exposed to excessive moisture or below grade. BX must always be grounded. The cable should be fastened with straps not more than 4 ft. apart and should be supported within 120 of an outlet box.
- Cap
- The upper limit of how much an interest rate or monthly payment can change, either at each adjustment anniversary date or over the life of the mortgage.
 |
Cape Cod Style |
-

- Carbon Monoxide
- Colorless, odorless, poisonous gas produced by incomplete fossil fuel (coal, oil, kerosene, natural or bottled gas) combustion. Termed a "chemical asphyxiant", it reduces the blood's ability to carry oxygen.
- Casement Window
- A hinged window which opens out from a building. (Sash opens on hinges at the sides)
- Caustic
- Strong chemical bases that can eat away or destroy and characterized by the presence of hydroxyl ions in solution
- CO
- See Carbon Monoxide
- CBS Construction
- "Concrete Block and Stucco" or "Concrete Block Structure. Preferred construction method in southern climates such as southern Florida, the islands of the Carribean and Central America. CBS construction is environmentally friendly, and provides a safer home during catastrophic weather such as tornados and huricanes. CBS homes are durable, quiet and energy-efficient.
- Celsius
- Metric temperature scale. Written as "C". Zero degrees C = 32 degrees F (fahrenheit) which equals the freezing point of water. The boiling point of water equals 212 F or 100 C. Conversion: (From C to F: X degrees C multiplied by 1.8 equals F). (From F to C: X degrees F multiplied by 5/9).
- CFC
- Chlorofluorocarbon. Chemical substances believed to cause depletion of ozone. Used as refrigerants and solvents - disposal of which is controlled.
- CFS
- Cubic Feet per Second. Moving water is measured in cfs units (well capacity)
- Chimney Pot
- Wide, extra tall chimneys with round or octagonal "pots" atop each flue. If there are multiple chimneys, they will each have separate flues and separate chimney pots. Chimney pots may be decorated. (also Tudor chimney)
-

- Clerestory
- The wall of a room or of a building that contains windows and rises above the roof.
- Coliform Index
- Purity of water (well-water) based on the amount of fecal bacteria.
- Columns
- Columns are often part of an overall structural system. Three of the basic column styles used for single family homes are taken from Greek architecture. (1) Corinthian columns show Egyptian influences in their "capitals" that are shaped like inverted bells and decorated with olive, laurel or acanthus eaves and rest on a base similar to that of the Ionic style. (2) The simplest Greek style is the Doric column (Parthenon in Athens). Features include fluted sides, smooth rounded top or capital and no separate base. (3) Ionic columns have scroll-shaped ornaments at the capital and rest on a rounded base.
- Composition Shingles
- Modern roofing material composed of asphalt, fiberglass fiber, or asbestos.
- Compost
- Organic fertilizer created from decomposted garbage and pollutant-free biodegradable trash.
- Condominium (Condo)
- You hold title to a particular unit or apartment in a multi-unit building with common areas owned jointly with the other condo unit owners. The unit itself is a separately owned space whose interior walls, floors and ceilings are the boundaries of the unit owned space. Get to know the requirements of the condo association, the monthly "condo fee" and the resale history of the condo unit you are considering before you buy.
- Concrete Block Structure
- "Concrete Block and Stucco" or "Concrete Block Structure. Preferred construction method in southern climates such as southern Florida, the islands of the Carribean and Central America. CBS construction is environmentally friendly, and provides a safer home during catastrophic weather such as tornados and huricanes. CBS homes are durable, quiet and energy-efficient. [MORE ABOUT CBS HERE]
- Concrete Slab
- A concrete slab (foundation) is an area or strip of concrete laid as a single unjointed piece to serve as the foundation for a home or building. It is reinforced with steel rebar or steel cables. It is supported entirely by surface soils.
- Conductivity
- The ability of a substance to conduct heat or electricity.
-

- Convection
- The transfer of heat energy between a solid and a fluid when their temperature differ.
- Corbel
- Supportive architectural bracket or block projecting from a wall.
- Corinthian Columns
- See columns
- Cornice
- The cornice is the uppermost section of moldings along the top of a wall or just below a roof. Often, a decorative molded projection at the top of a wall, window or construction. The upper part of an entablature and consists of the angular raking cornice at the top, and the horizontal cornice along the bottom.
- Corrosion
- Most alloys corrode just from the moisture in the air. Dissolving of metal is caused by a chemical reaction between water and the pipes that the water contacts, chemicals touching a metal surface, or contact between two metals. The weakening of steel due to oxidation of the iron contained in the steel is called electrochemical corrosion.
- Cupola
- Dome shaped roof on a circular base set on the ridge of a roof.
- Crawl Space
- In homes or buildings without a cellar and not built totally on a slab or cement pad, the floor may be raised above the ground to allow access to utilities (plumbing, wiring) or insulation.
- Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM)
- The measure of the volume of a substance flowing through air within a fixed period of time. Used in specifications for indoor air quality to refer to the amount of air, in cubic feet, that is exchanged in a minute's time. (rate of flow)
- Curing
- The process in which mortar and concrete harden. Time needed for curing depends upon the type of cement, mix proportion, required strength, size and shape of the concrete section, weather and exposure conditions. Curing may take 3 weeks or longer for lean concrete mixtures used in structures such as dams or it may be only a few days for richer mixes. Favorable curing temperatures range from 50 to 70 degrees F° Design strength is achieved in 28 days.
-

- Deco
- See Art Deco.
- Deed of Trust
- Deed in which the Borrower promises real property as guarantee for the repayment of a loan. The parties named in a deed of trust are the Trustor, Trustee, and Beneficiary.
 |
Dentil |
- Decorative
- Ornamental. Not required for the operation of the essential systems and components of a home.
- Describe
- To report a system or component by its type or other observed, significant characteristics to distinguish it from other systems or components.
- Denitrification
- Conversion of nitrate into nitrogen gases under anaerobic conditions, resulting in loss of nitrogen from ecosystems. The return of nitrogen from decomposed matter to the atmosphere by bacteria that change nitrates to nitrogen gas.
- Dismantle
- To take apart or remove any component, device or piece of equipment that would not be taken apart or removed by a homeowner in the course of normal and routine home owner maintenance.
- Doric Columns
- See columns
 |
Dormer |
 |
Double Hung Window |
- Drywall
- A system of interior wall finish using sheets of gypsum board and taped joints. Standard width is 48 inches with lengths of 8 ft and 12 ft. Also called sheetrock.
- Ducts, Ducting
- A system of shafts or tubes designed to allow for the circulation of air (hot air heating systems) or designed to carry and protect cables or pipes. In most residencces, ducting is enclosed and inaccessible in living areas, but may be accessible in basement or attic spaces
- Due-on-Sale Clause
- An acceleration clause that requires full payment of a mortgage or deed of trust when the secured property is sold or changes ownership through other means.
- Dutch Colonial
- An American style home that began with the German, or Pennsylvania-Dutch beginning in the 1600s. Broad gambrel roof with flaring eaves that extend over the porches marks the style - and creates an appearance like a barn. The chimney is usually placed on one or both ends with double-hung sash windows with outward swinging wood casements and dormers with shed-like overhangs.
-

- Earthship
- A passive solar home made of natural and recycled materials which takes advantage of a thermal mass construction for temperature stabilization that utilizes renewable energy sources & integrated water systems - and attempts to have the capability to exist outside the commercial or government energy & water sources.
- Eaves
- The lower edge of a sloping roof; that part of a roof of a building which projects beyond the wall. Boxed eaves are a simple cornice treatment where the eaves of a pitched roof are boxed in with wood and have few other details. Exposed eaves reveal the structure of the roof through exposed rafters. Bracketed eaves consist of large scroll brackets that decorate the cornice.
- Elevation
- a series of measurements to determine the difference in height between a central point and other points.
- Engineering Service
- Any professional service or creative work requiring engineering education, training, and experience and the application of special knowledge of the mathematical, physical and engineering sciences to such professional service or creative work as consultation, investigation, evaluation, planning, design and supervision of construction for the purpose of assuring compliance with the specifications and design, in conjunction with structures, buildings, machines, equipment, works or processes.
- EPA
- The Environmental Protection Agency leads the nation's environmental science, research, education and assessment efforts: develops and enforces regulations; offers financial assistance to States, non-profits and educational institutions to support high-quality research that will improve the scientific basis for decisions on national environmental issues; performs environmental research; sets voluntary pollution-management goals such as conserving water and energy, minimizing greenhouse gases, slashing toxic emissions, re-using solid waste, controlling indoor air pollution, and getting a handle on pesticide risks; advances educational efforts to develop an environmentally conscious and responsible public, and to inspire personal responsibility in caring for the environment; and publishes written materials to assist these efforts.
- Eutrophication
- Natural eutrophication is the process by which lakes gradually age and become more nutrient rich. It normally takes thousands of years to progress. However, humans, through their various cultural activities, have greatly accelerated this process in thousands of lakes around the globe creating nutrient pollution from runoff from agricultural fields, field lots, urban lawns, golf courses, and untreated, or partially-treated, domestic sewage. Sewage was a particular source of phosphorus to lakes when detergents contained large amounts of phosphates. The phosphates acted as water softeners to improve the cleaning action, but they also proved to be powerful stimulants to algal growth when they were washed or flushed into lakes. These "algae blooms" lead to changes the water quality in a lake - bringing oxygen depletion and resultant fish kills. (See BOG)
- Evapotranspiration
- The combination of water that is evaporated and transpired by plants as a part of their metabolic processes. Reference evapotranspiration is the amount of water needed for plant growth in a year of average weather.
- Eyebrow dormer
- Dormer on the slope of a roof that has no sides with the roofing carried over it in a wavy line.
- Facade
- The elevation or face of a building.
-

- Fanlight
- A semicircular or semielliptical window over the opening of a door or another window, with bars radiating outward in the form of an open fan. (Sunburst light)
- Fascia
- Horizontal, flat trim pieces that are used around the outer end of roof rafters at eave/wall junctures or board connecting the ends of the roof rafters and providing a surface to support gutters.
- Fenestration
- Arrangement or design of windows and doors in a building.
- Feng Shui
- Feng shui ("fung shway") is an intuitive art art form employed by decorators and architects to create harmony and balance in the living environment.
- Firewall
- A fire-resistent wall constructed between specific areas built to restrict or prevent the spread of fire between the two areas. Generally constructed with a 5/8 inch type X drywall on one side and a 1/2 inch regular drywall on the other side. Firewalls are required by local fire codes. Firewalls are rated by how long they are expected to hold back a fire on either side of the wall. A 2 hour fire rating requires two layers, and a 3 hour rating requires three layers of type X drywall. Drywalls are often built, when a garage is attached to a house, between the two structures, firewalls can also be required between some ceilings and upper floors. Check with your local fire marshall or building/code officials.
- Flat Arch
- See Arches
- Fluted Column
- Parallel grooves or channels decorating the shaft of a column.
- Flying Buttress
- See Buttresses.
- Footing
- Any physical object (such as a Bell Bottom Pier) that provides support for a home foundation by distributing the weight over a greater area of the supporting soil and, thus, prevent settling. Generally made of concrete and used under chimneys and columns as well as under foundation walls. In northern climates, footings are placed below the frostline to prevent movement during freezing
- Footprint
- The outline of a building's ground plan from a top view.
-
Foundation

- A home foundation is that part of the structure that is in direct contact with the ground. The foundation transmits the weight of the entire home and itself to the supporting soil.
- Foursquare
- See American Foursquare.
- Framing System
- The framing system is made up of the support system for the floors, ceilings, walls, and roof. Timber is used for most home construction, although a few use metal.
- Fungi
- Fungi are plant-like organisms that lack chlorophyll.
- Further Evaluation
- Examination and analysis by a qualified professional, tradesman or service technician beyond that provided by the home inspection.
- Gable
- A triangular wall segment at the end of a double-pitched or gabled roof. A gabled roof is a pitched roof having a gable at each end. A bell gable is a small turret placed on the rise of a church roof to hold one or more bells.
- Gable Rafters
- Gable rafters (also called gableboards, bargeboards, barge rafters, vergeboards, and fly rafters protrude down from the projected end of a roof.
- Gambrel Roof
- A double-sloped gable roof, which allows additional living or storage space.
- Geodesic
- Latin - meaning "earth dividing" - a geodesic line is the shortest distance between any two points on a sphere.
- Geodesic Dome
- R. Buckminster Fuller was the creator for the sphere-like structure called a geodesic dome. The dome is composed of a complex network of triangles that form a framework that is self-bracing and provides structural strength with a minimum of material. Geodesic domes are efficient, can be built low-cost and are durable. Geodesic domes are used for emergency shelters, weather stations and mobile military housing.
 |
Georgian style house |
-

- GFI or GFCI
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters are special devices capable of opening a circuit when even a small amount of current is flowing through the grounding system. It protects a person rather than the circuit by being much faster and more sensitive than either a fuse or circuit breaker.
- Gothic Arch
- See Arches
- Gothic Architecture
- Gothic architecture was dominant in France and the western half of Europe in the 12th through the middle of the 16th centuries. Gothic Architecture features include progressive lightening and heightening of structure, pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, walls reduced to a minimum by spacious arcades, gallery or triforium, and by spacious clerestory stained glass windows.
- Gothic Revival
- Gothic Revival is an architectural phase of the Romantic Movement, which looked back upon and idealized the past, and emphasized emotions, spontaneity, individuality and freedom. Gothic Revival style was used for cottages, villas, and country cottages. Gothic features include gingerbread trim along the eaves and gable edges, steeply pitched gable roofs, wall dormers, hood molds over the windows.
- Graduated Payment Mortgage
- Monthly payments start at a lower level and increase at a predetermined rate.
- Greek Revival
- This style can be recognized full-height entries, or full-building width porches, entryway columns sized in scale to the porch type, and a front door surrounded by narrow rectangular windows. Roofs are generally gabled or hipped. Roof cornices sport a wide trim
- Greenboard
- Wallboad manufactured for use in moist rooms such as bathrooms.
- Greywater
- Wastewater from clothes washing machines, showers, bathtubs, hand washing , lavatories and sinks. See blackwater.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters
- GFCI devices are capable of opening a circuit when even a small amount of current is flowing through the grounding system. It protects a person rather than the circuit by being much faster and more sensitive than either a fuse or circuit breaker.
- Gypsum board
- Panels or slabs consisting of a non-combustible gypsum core, surfaced and edged with covering material designed for various uses with respect to performance, application, location and appearance. They include wallboards, sheathing, backing boards, green boards, & form boards.
- Half-timbered
- Exposed wood framing with the spaces between the wooden timbers filled with plaster, brick, or stone characterizes this construction style.
- Hip Roof
- A roof with four uniformly pitched sides sloping sides and ends.
- Home Inspection
- The process by which an inspector visually examines the readily accessible systems and components of a home and which describes those systems and components in accordance with these Standards of Practice.
- Hood Molding
- Molding that projects out over a doorway or window or off a face of a building to divert rain.
-

- Horseshoe Arch
- See Arches
- Household Appliances
- Kitchen, laundry, and similar appliances, whether installed or free-standing.
- Ionic Columns
- See columns
- Inspect
- To examine readily accessible systems and components of a building in accordance with these Standards of Practice, using normal operating controls and opening readily openable access panels.
- Inspector
- A person hired to examine any system or component of a building in accordance with these Standards of Practice.
- Installed
- Attached such that removal requires tools.
- Italianate
- Mostly 1850-1880. Ornate homes featuring symmetrical bay windows, small chimneys set in irregular locations, tall, narrow, windows, and towers. Elaborate window designs that are repeated in the columns, and door frames.
- Interest Rate
- The cost of borrowing money. Interest rates can be adjustable or fixed. A variety of rates and conditions exist.
- Jack Arch
- See Arches
- Keystone
- Central block, called a voussoir, of an arch without which an arch will not support itself. Today, keystones are used ornamentally and are not needed to support an arch.
- Knee Brace
- A wooden triangular brace that supports the eaves of a building. Knee braces were frequently utilized in the construction of Bungalow style residences.
- Label molding
- Projecting molding such as a dripstone or hoodmold that extends horizontally across the top of an opening and returns vertically downward for a short distance forming an "L" and inverted "L" at the bottom of the molding that acts as a stop for rain. Found on wall faces, above arches, doorways and windows.
- Leach Field
- Porous soiled area with lines from the septic tank running through it. Treated liquid waste is forced from the tank and percolates down through the soil.
- Lien
- A claim or hold on a property or other asset that was agree upon as a security against a loan or debt.
- Lintel
- A horizontal beam located above a window or door. Referred to as a "structure member", the lintel supports the weight of the wall above it.
- Load Bearing Capacity
- Refers to the maximum load or weight that can be applied to the soil before movement or failure (shear failure). The soil under the home foundation is under constant pressure from the weight of the home.
- Loan Commitment
- An agreement to make a loan for a specified amount with specified interest and repayment terms.
-

- Loan to Value Ratio
- The relationship between the mortgage amount and the appraised value of the property.
- Locks
- Four commonly used lock systems: (1) Keyed-knob locks, although common exterior door locks, are easily jimmied. Look for ones that have a hardened steel pin with the beveled latch called a deadlocking latch. (2) Deadbolt locks are a good way insure entrance security. Look for a bolt of at least one inch with a rotating steel pin in the bolt for resistance and a free-spinning brass cover over the outside cylinder. (3) Full mortise locks should be installed by a professional locksmith and can consist of double locks - including a deadbolt. (4) Rim-mounted locks, "vertical deadbolts", go on the interior surface of the door.
- Lock-in
- A written agreement that guarantees the home buyer a specific interest rate on a home loan as long as the loan is closed within a certain period of time and may specify the number of points to be paid.
- Louver
- A door or window comprised of overlapping downward sloping slats, which shed rain while admitting light and air.
- Low E windows
- Low E & Argon Gas form insulating glass units that reflect heat back into the room and increase energy-saving efficiency by stopping heat loss through the window in the winter and re-radiated solar heat from entering your home in the summer. Special coatings reduce direct summer sun rays and block fabric-fading ultraviolet rays.
- Mansard roof
- Each side of a mansard roof has two slopes. The lower slope of the pair on each side is steeper with the upper slope unseen from the ground. Dormers may be put into the lower slopes.
- Masonry
- Masonry or masonry brick refers to block, or stone which is secured with mortar.
- Meeting Rail
- Part of window where two sets of panes meet and overlap.
- Moorish Arch
- See Arches
- Mortgage Life Insurance
- Term life insurance sold to mortgagors that covers the amount due on the mortgaged property at the time of the mortgagor's death. This insurance has limited value. It's "payout" decreases as the mortgage balance decreases and it automatically paid to the mortgagee (lender). Consider other ways or insurance options to provide the necessary funds to continue mortgage payments on the event of the death of one of the mortgagors (borrowers).
- Mortgagee
- The person, bank or mortgage company that loans the money in a mortgage loan transaction - the lender.
- Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP)
- Insurance for an FHA loan paid by the borrowed (mortgagor).
-

- Mortgagor
- The one who borrows the money to buy property - and agrees to lien the property as a security against payment of the loaned sum.
- Muntins
- Secondary framing member that holds and separates the panes in a sash.
- Normal Operating Controls
- Devices such as thermostats, switches or valves intended to be operated by the homeowner.
- Newel
- Tall ornamental post that supports the railing at the head or foot of a stair.
- Ocular Window
- Rounded window (English).
 |
Oriel Window |
- Pane
- A piece of glass in a window.
- Parapet
- A solid protective or decorative low wall located along the outside edge of a roof. A parapet projects from the edge of a platform, terrace, or roof, and some will rise above the cornice of a building.
- Pediment
- In classical architecture a low-pitched triangular gable above a facade, or a smaller version over porticos above the doorway or above a window. A triangular gable end of the roof above the horizontal cornice.
- Percolation Test
- Soil test to determine if the soil can absorb and drain water adequately for the use of a septic system for sewage disposal.
- Platform Framing
- Most modern residential and light commercial designs use platform framing. The first floor is built on top of the foundation walls like a "platform". The walls are then constructed and raised on the platform and the second story floor or platform is built on the raised walls.
- Pilaster
- Decorations that look like pillars but do not add support.
-

- Pitch
- The "pitch" is the steepness of roof slope.
- Pivot Window
- A hinged window which opens out with the aid of a mechanical crank.
- Portico
- A porch or walkway with a roof supported by columns, often leading to the entrance of a building. Porticos generally cover the door but are not large enough to create an outdoor seating area. Porticos can also be two stories high.
- Post and Beam
- Post and beam framing construction often found in rustic type of housing or exotic homes. This style of framing lends itself to large open areas. Posts are the upright timbers used to support the roofing system and form the exterior walls. Beams are horizontal timbers used to tie the structure together and support live loads. Post and beam framing is often referred to as timber frame construction as well.
- Prairie Box Homes
- Prairie architecture pioneered by Frank Lloyd Wright were one-story homes with features such as, an open floor plan, rows of small windows, a low-pitched roof with overhanging eaves, and a central chimney. (Also see American Foursquare)
- Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI)
- Insurance that is paid for by the mortgagor (borrower) to protect the mortgagee (lender) against the mortgagor's default on the loan. It is generally only required when the down-payment on the loan is less than a certain percentage of the sale price/mortgage amount.
- Rafter
- A wooden member of a roof frame which slopes downward from the ridge line.
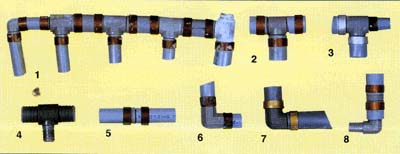 |
Polybutylene piping Polybutylene is a form of plastic resin that was used extensively in the manufacture of water supply piping from 1978 until 1995. Due to the low cost of the material and ease of installation, Polybutylene piping systems were viewed as "the pipe of the future" and were used as a substitute for traditional copper piping. It is most commonly found in the "Sun Belt" where residential construction was heavy through the 1980's and early-to-mid 90's, but it is also very common in the Mid Atlantic and Northwest Pacific states. |
- Readily Accessible
- Available for visual inspection without requiring moving of personal property, dismantling, destructive measures, or any action which will likely involve risk to persons or property.
- Readily Openable Access Panel
- A panel provided for homeowner inspection and maintenance that is within normal reach, can be removed by one person, and is not sealed in place.
- Rebar, Steel Rebar
- Ribbed steel bars installed in foundation concrete walls, footers, and poured in place concrete structures designed to strengthen concrete. They are used to increase the tensile strength of concrete. Rebar comes in standard lengths of 60 ft. They are cut to length and bent as required. All bars must be bent without heating except as permitted by the engineer. #5 rebar means that it has a diameter of 5/8 inch, #4 rebar means that it has a 4/8 inch or 1/2 inch diameter. #4 is the minimum size that can be used for a single family residence. Rebar should be tied to prevent shifting during the pouring of concrete.
- Recreational Facilities
- Spas, saunas, steam baths, swimming pools, exercise, entertainment, athletic, playground or other similar equipment and associated accessories.
-

- Reinforced Concrete
- A combination of steel and concrete using the best properties of each. The steel consists of rebar or reinforcing bars varying from 3/8 inch to 2 1/4 inch in diameter and is placed before concrete is poured.
- Report
- To communicate and/or document in writing.
- Representative Number
- A sampling. One component per room for multiple similar interior components such as windows and electric outlets; one component on each side of the building for multiple similar exterior components.
 |
- Ribbon windows
- A band or series of single windows (3 or more) placed directly next to one another and separated only by mullions forming the appearance of a band or "ribbon" across the front of a building.
- Ridge
- The highest part of a roof.
- Roof Drainage Systems
- Components used to carry water off a roof and away from a building.
- Roman Arch
- See Arches
 |
|
 |
- Salt Box Style
- A New England Colonial with a sharply sloping gable roof that resembles boxes once used for storing salt. The step roofline drops dramatically from two and one-half stories in front to a single story in the rear. Square or rectangular in overall shape. Features include a large central chimney, large double-hung windows with shutters, and exterior walls made of clapboard or shingles.
- Sash
- A frame that encloses the panes of a window.
- Segmental Arch
- See Arches
- Settlement
- Refers to a process or situation where part of a home's foundation has moved below its original elevation. It usually results in interior and exterior cracks in various places throughout the home. [See Upheaval]
-

- Shed Dormer
- The dormer and the roof slope in the same direction. Simulates the salt box roofing style.
- Sheetrock
- Another name for drywall or wall board.
- Shut Down
- A state in which a system or component cannot be operated by normal operating controls.
- Sick Building Syndrome
- Indoor transmission of infectious agents. Chemical(s) or other material(s) found in the interior environment are causing the symptoms of illness or allergy in the buildings occupants or in those who spent significant time in the building regularly or who are exposed to on a one-time basis to a particularly potent or poisonous element. Also see building-related illness
- Significantly Deficient
- Unsafe or not functioning.
- Sliding Window
- Sliding windows include one or more horizontal operating sashes in a master frame and do not protrude out. They are available with fixed lights and operable sashes.
- Solid Fuel Burning Appliances
- A hearth and fire chamber or similar prepared place in which a fire may be built and which is built in conjunction with a chimney; or a listed assembly of a fire chamber, its chimney and related factory-made parts designed for unit assembly without requiring field construction.
- Split-Level Style
- Modern styled architecture that separates living activities - each on one level, with the levels being only a 1/2 story distance up/down.
- Square-foot Appraisal Method
- Estimating building costs by multiplying the number of square feet being appraised by the cost per square foot for similar construction. (sf X $ p/sf=total cost)
- Stachybotrys
- Stachybotrys chartarum is a fungus that has become notorious as a mycotoxin producer that can cause animal and human mycotoxicosis. Stachybotrys is a greenish-black mold that grows well on materials with a high cellulose content such as wall studs, dry wall, and ceiling tiles that are exposed to water and excessive humidity. Evidence has accumulated implicating this fungus as a serious problem in homes and buildings and one of the causes of the "sick building syndrome.". [More on Stachybotrys]
- Stem Wall
- Short concrete extension of the slab foundation, 6 to 12 inches vertically, that usually surrounds the perimeter of the building. Stem walls are built to keep outside water from getting inside.
- Straight Arch
- See Arches
- Structural Component
- A component which supports non-variable forces or weights (dead loads) and variable forces or weights (live loads).
- Stucco
- A masonry material applied as exterior wall fabric.
-

- Syrian Arch
- See Arches
- System
- A combination of interacting or interdependent components, assembled to carry out one or more functions.
- Technically Exhaustive
- An investigation that involves dismantling, the extensive use of advanced techniques, measurements, instruments, testing, calculations, or other means.
- Timber Frame Construction
- Post and beam framing is often referred to as timber frame construction as well.
- Title Insurance Policy
- Insurance policy that protects the mortgagee or other party against losses.
- Tongue & Grove
- A type of flooring, siding, or ceiling or wall covering in which the tongue of one board is joined to the grove in another board.
- Transit
- A surveyors instrument that establishs points and elevations both vertically and horizontally. Used to plumb walls or to measure the angle of elevation from a horizontal plane.
- Transom
- Window above a door or a horizontal crossbar in a window or between a door and a window.
- Trompe L'oeil
- Trompe l'oeil translates "to fool the eye" in french. It is a phrase used to describe decorative painting that creates an illusion that mimics reality. Trompe l'oeil art can be found on buildings, furniture, posters, murals - almost anything - and gives the appearance of three-dimensional or photographic realism.
- Truss
- Rigid framework composed of a combination of members in a triangular arrangement. Allows large interior area without supporting members
- Tudor Arch
- See Arches
- Tudor Chimney
- See Chimney Pot
- Tudor Style
- Dating from the 1920s and 1930s marked by the "half-timbering" on bay their windows and upper floors. Facades have one or more steeply pitched cross gables. Features include rounded doorways, patterned brick or stone walls, multi-paned casement windows and large stone chimneys.
- Under-floor Crawl Space
- The area within the confines of the foundation and between the ground and the underside of the floor.
- Underlayment
- Secondary roofing layer that is waterproof or water-resistant installed on the roof deck and beneath shingles or other roof-finishing layer.
-
Upheaval

- refers to a process or situation where part of a home's foundation has moved above its original elevation. It usually results in interior and exterior cracks in various places throughout the home. [See Settlement )
- Unsafe
- A condition in a readily accessible, installed system or component which is judged to be a significant risk of personal injury during normal, day-to-day use. The risk may be due to damage, deterioration, improper installation or a change in accepted residential construction standards.
- Valley shield
- Underlayment for added protection in the heavy water flow areas of a roof or valley (angle formed by the junction of two sloping sides of a roof)
- Vault/Vaulted
- Arched or domed shaped ceiling or roof
- Veneer
- A covering of one material over another. Usually a more expensive material is used over a less expensive material for an improved appearance. On an exterior, bricks or stone might be used to cover concrete or quality wood over plywood.
- Vent
- Any outlet that allows air to rise up and out of the structure. Vents may protrude through the roof deck, such as a pipe or stack,or through an exterior wall. Vents and venting fans are also installed on the roof, gable or soffit for the purpose of ventilating the underside of the roof deck.

- Veranda
- A covered porch, balcony, platform or deck. Verandas can be quite elaborate, roundaround the house or building. Many have have ceiling fans to extent their use during hot weather.
- Vestibule
- Enclosed entry to a building
-

- Voltage
- A measure of electrical potential. To arrive at the voltage, divide watts by amps. Most residences are wired with 110 and 220-volt lines. 110-volt power is used for lighting and most of the other circuits. 220-volt circuits are for appliances such as a stove or clothes dryer.
- Voussoir
- Term for the wedge-shaped blocks forming the curved parts of an arch or vaulted ceiling. The central voussoir is the keystone.
- Wallboard
- Also known as drywall or sheathing. Inexpensive building material made of gypsum that's formed into a flat sheet and covered with heavy paper. Sheets commonly come in 8 ft, 10 ft, 12 ft, or 14 ft lengths that are 4 ft wide. See green boards.
- Water Heating Devices
- There are a wide variety of residential electric water heaters that range in capacity from fifteen to one hundred gallons. They can be expected to last at least as long as their warranty, or from five to eight years, but they will generally last longer. However, few of them last longer than fifteen or twenty years and many eventually leak. So it is wise to have them installed over a drain pan, and preferably plumbed to the exterior. Also, they can be dangerous if they are not seismically secured and equipped with a pressure/temperature relief valve and discharge pipe plumbed to the exterior.
- Window Styles
- Window styles: (1) Bay -circle bay and box bay- (2) Casement (3) Label mold (4) Ribbon (5) Oriel (6) Paired (7) Hood Mold (8) Palladian and (9) Double-Hung (10) Sliding Windows (11) Low E & Argon Gas.
- Wiring Methods
- Identification of electrical conductors or wires by their general type, such as "non-metallic sheathed cable" ("Romex"), "armored cable" ("bx") or "knob and tube", etc.
-

- Zoning
- Town, county or state regulations that specify the limitations on the use of property. Generally, towns set aside certain parcels of land designed to be developed for strictly industrial or commercial use to avoid mixing residential properties with properties dedicated for dangerous or heavy-use. Downtown often carry strict zoning, as do area surrounding schools.



